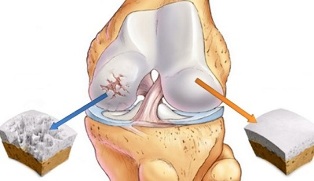
Arthritis is a degenerative joint disease, accompanied by dystrophic processes of cartilage tissue. As the disease progresses, the sacrum, ligamentous apparatus, synovial membrane, and the closest skeletal structures also participate in the destruction process.
The incidence of joint diseases
The majority of people with joint disease are the elderly. The disease after the 65-year-old mark is not only the most commonly diagnosed joint disease, but also the main cause of later disability. Furthermore, in old age, most women get the disease, but among young people, the majority of people with the disease are men.
In different countries, the incidence of osteoarthritis varies greatly. The reasons for the widespread popularity of statistical data cannot be determined yet.
Causes and Risk Factors
Osteoarthritis is a disease that can be primary or secondary. If there is no objective reason for the development of the pathology, they talk about the main type. If it was possible to identify the cause of the joint disease, they talked about the secondary type.
Secondary joint disease can be triggered by the following negative factors:
- trauma to joints of different nature (frequent falls, sprains, bruises);
- chronic congenital tissue dysplasia;
- pathological changes in metabolism;
- various autoimmune diseases;
- nonspecific inflammatory processes in the joint region;
- certain pathologies of the endocrine system organs;
- processes are of the degenerative-dystrophic type, occurring chronically;
- various diseases, accompanied by excessive joint mobility, with weak ligamentous apparatus;
- present hemophilia;
- specific type of inflammatory process.
In addition to the immediate causes, which lead to the development of joint disease, there are also basic factors that do not self-induce disease, but may increase the risk of developing the disease.

These include:
- over 55 years old;
- excess weight, so the load on the joints increases;
- loads too much on a joint or group in case of improper sports training, specific work being in a long position;
- history of joint surgery; Genetic
- ;
- hormonal changes in the postmenopausal female body;
- persistent hypothermia;
- pathology of the spine not treated;
- does not absorb enough useful macro and trace elements from food.
Development Mechanism
The mechanism of the development of joint disease is well known. Cartilage, which ensures normal contact of two bones, is naturally smooth, without abnormalities or roughness, helps to maintain normal movement of joints. When infected, the structure of cartilage changes, becomes rough, defects appear to decrease the natural sliding efficiency.
Due to the unevenness, the cartilage is gradually injured, some places calcify, and some places liquefy. In this case, it is possible to separate tiny particles that end up in the synovial fluid and possibly damage surrounding tissues.
As the condition worsens, the joint can go into a chronic degenerative state, significantly impairing the motor function of the joint.
Degrees
Doctors divide joint disease into three main degrees:
- I degree.Characterized by the absence of a clear clinical picture. Patients may have rare manifestations of pain in the affected joint, but usually do not consult a doctor. At the same time, there were changes in the muscle-ligament apparatus and in the synovial fluid, but the defects were not seen.
- degree II.Symptoms of joint disease become more pronounced. Pain is typically bearable, but frequent. The patient visits a doctor when he notices a decrease in quality of life. A characteristic crack can be heard in the affected joint. Changes are observed in neighboring muscle structures, since nerve conduction is disturbed.
- degree III.Characterized by phonetic markers. Joint cartilage is very thin, can find cysts, calcifications or chemicals in it. The ligamentous apparatus becomes shorter, resulting in increased mobility in the affected area, accompanied by a restriction due to the pronounced inflammatory process. The metabolism of surrounding tissues is affected, which can lead to muscular dystrophy.
In all cases, the patient will need to clarify the diagnosis from the attending physician. This is due to the specificity of the course of the disease, which is characterized by periods of remission and cure, alternating.
Suffering from illness
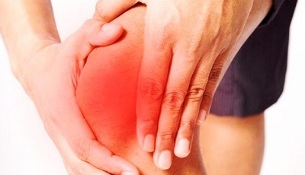
Joint pain is the most common complaint patients see. Their characteristic feature is connection with the time of day, the weather, and physical activity.
In most patients, pain is exacerbated by walking, running or other physical activity directed at the affected joint. As soon as the load stops, the pain gradually subsides. Their development is explained by the inability of the cartilage to perform shock-absorbing functions.
At night, discomfort most often occurs due to blood accumulation in the veins. Another reason is the increase in pressure during this period.
One of the primary diagnostic criteria is that the presence of so-called pain begins to disturb the patient as soon as they begin to exercise. The pain that starts usually goes away with continued physical activity. Their appearance is explained by the presence of joint deposits (debris) that irritate nerve ends. As soon as these deposits move out of the nerve, the pain goes away.
Symptoms
In addition to pain, doctors identify other signs of joint disease, which in turn may suspect pathology.
These include:
- Painful and crunchy sound.Lomota mainly occurs when a person has hypothermia. At first, the cracking sound will be difficult to hear at first, but as the disease progresses without treatment, those around you will hear it.
- Reduced mobility. In the early stages of the development of the pathology, there is no decrease in mobility. However, the longer the disease is left untreated, the stronger the movement restriction of the joint becomes. This is explained because joint space is narrowed and the closest muscle structures constrict.
- Joint deformation.This is characteristic of late-stage arthritis, but is also an important indicator of the course of the disease. During this period, it was very difficult to treat the disease.
Which doctors treat the joint?
Who treats arthritis? In most cases, a number of specialists are involved in therapy. First of all, there is the participation of a joint specialist, a joint specialist. In addition, the patient will also need to see an orthopedic doctor. If the disease is the result of an inflammatory process, you should also see a rheumatologist.
If necessary, other specialists may be involved during treatment. Usually, you have to seek the service of trauma, physiotherapists, massage and surgical doctors.
Diagnosis
Treatment of arthritis begins only after the diagnosis is confirmed and the extent of the pathology has been determined. First of all, the doctor interviews patient details and conducts examination. The presence of characteristic complaints and defects indicates that there is a disease.
X-rays of the affected joint are required to confirm a diagnosis. If the disease affects the knee, then take a photo of the knee, if the pathology is found in the hand, then the X-ray signs of the disease will be specifically searched there.
X-ray diagnosis does not always give a complete diagnosis of a patient. In this case, he may be sent for an MRI scan (this will allow an assessment of the state of soft tissues and their participation in the pathological process) or CT (this will help to give a resulton the state of bone and cartilage structures, participation of the most recent anatomical structures in the pathological process).
Treatment
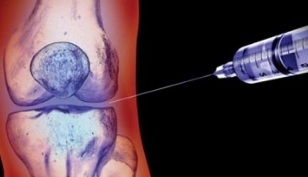
How to treat dry joints? Choosing the appropriate treatment technique depends on the severity of symptoms and the stage of the disease.
The doctor chooses the treatment regimen after evaluating the general condition of the patient and the course of the disease. Both conservative and surgical treatments can be used.
Medicines
How to treat the disease if you don't want to have surgery but use drugs?
Conservative therapy is only suitable for patients at an early stage of disease and will include the use of three main classes of drugs:
- glucocorticosteroid- hormonal drug that effectively reduces the inflammatory process during exacerbation, is injected into the joint cavity;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,are mainly injected and injected into a muscle near the joint or directly into a vein. But doctors may also recommend pills, although this option for taking NSAIDs is undesirable due to its negative effects on the gastrointestinal tract;
- chondroprotectors- drugs of this group can reduce the destruction of cartilage tissue and enhance regeneration, especially effective at the early stages of disease formation.
Surgery
How to cure joint disease if the disease has gone too far? In this case, conservative therapy will be ineffective, and doctors may only recommend surgery to the patient.
Laparoscopy is done in most cases today. During the operation, the real joint is replaced by a prosthetic joint, which fully functions of a healthy joint.
In some cases, palliative therapy options are provided, the main task being to reduce the load on the joint surface.
Exercises
In the early stages of the disease, it is not only treated with drugs but also with physical therapy exercises. Exercise is an important phase of treatment to help maintain joint function and reduce the likelihood of further disease progression.
Depending on the severity of the pathology and the individual characteristics of the patient, the exercise set is individually selected. The doctor must take into account the positioning of the joint, allowing the most effective impact on the affected tissues.
Should not be self-taught without medical supervision, especially at an early stage. Exercises must be selected to be as smooth as possible without sudden movements.
Exercise therapy classes are only effective if the patient dedicates a little time to the recommended therapy every day.
Traditional method

Many people with joint problems refuse to use drugs or surgery until the very last moment. In this case, alternative medicine is used to replace the curative medicine.
The most commonly used plants in therapies are:
- Kalanchoe;
- ginger;
- hell;
- laurel leaves;
- garlic;
- cinnamon;
- horsetail and others.
They are used in the form of tincture, decoction, and medicine applied to the affected area. It is important to remember that the disease cannot be completely treated with homemade recipes. Folk remedies are best combined with traditional medicine.
Precautions
What to do to reduce the likelihood of arthritis in old age? Simple precautions available to anyone.
Recommended:
- moderate daily physical activity: walking, cycling, simple exercises like charging, etc. v. ;
- adheres to the basic principles of healthy eating: eat often, but sparingly, avoid fast food, overeating, heavy and fatty foods, eating spicy foods;
- weight control: weight gain leads to increased stress in the joints, possibly joint syndrome;
- promptly treat chronic diseases leading to metabolic disorders;
- use of vitamin and mineral complexes in cases where the amount of nutrients provided from food is considered insufficient.
The difference between osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis
Many people confuse arthritis and osteoarthritis due to the same sound. However, these are completely different diseases.
Arthritis is not dystrophy and degeneration in joint tissues, but any inflammatory reaction that can develop in the joint cavity, regardless of its cause. Inflammation usually affects not only the joint, but also the closest muscles, bone structures, and ligaments. Pain in arthritis is not related to exertion, it can disturb the patient even with rest and no cracking sound in the joints.

In most cases, it is impossible to distinguish arthritis from arthritis independently, since the main symptom is pain and the patient rarely knows its features for each pathology.
It is better to delegate an accurate diagnosis to the attending physician so as not to make mistakes in the treatment and prevention of the next disease.
Arthritis is a dangerous condition that can lead to disability if the patient does not see a doctor in time. When there are the first signs of the disease, a specialist should be contacted to confirm the diagnosis and choose the most optimal treatment.
If it is possible to detect the disease at an early stage, it can be cured even without surgical intervention, limited to conservative treatment.





































