Bone tumor -degenerative-dystrophic damage to the tissues of the spine, characterized by damage to the discs, adjacent articular surfaces and vertebral bodies, the ligamentous apparatus of the spine.
Usually, the pathological processes in osteonecrosis primarily affect the bones and ligaments. The fact that the disease has already begun, we usually learn when complications appear - pain, sensory disturbances, muscle atrophy, disruption of internal organs.
Who gets osteonecrosis?
Today, between 40 and 90% of the world's population has osteonecrosis. Usually, the disease affects people over the age of 30. However, the first symptoms of osteonecrosis may appear in adolescence.
Developmental stages of osteonecrosis of the spine
- The first stage in the development of osteonecrosis.
Dehydration of the nuclear bone marrow begins. This results in a decrease in the height of the disc. Cracks appear in the annulus (annulus fibrosus), but the pathological process does not extend beyond the disc.
- The second stage in the development of osteonecrosis.
As a result of the decrease in disc height, the attachment points of muscles and ligaments of two adjacent vertebrae become closer together. As a result, the muscles and ligaments sag. This can lead to excessive mobility of the two vertebrae relative to each other, i. e. instability of the vertebral motor segment is formed. This stage is characterized by the sliding or displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other along with the formation of vertebrae.
- The third stage in the development of osteonecrosis.
During this stage, the most obvious morphological changes occur, which are mainly related to the discs themselves: the discs prolapse and protrude. The joint apparatus of the vertebrae - the motor segment is also affected. In disc joints and non-vertebral joints, vertebrae degeneration occurs, forming a degenerative joint process.
- Fourth stage in the development of osteonecrosis.
At this stage, adaptive changes occur in the affected spinal segments. The body tries to overcome the excessive mobility of the vertebrae, immobilizing the spine to maintain its supporting and protective functions. In this regard, marginal bony outgrowths occur on the adjacent surfaces of vertebral bodies, or in other words, osteogenic cells. A bone cell grows "in the wrong place" causing micro-altering of the nerve root. In the fourth stage, the capsular process usually begins in the discs and joints. In the end, the vertebral motor segment turned out to be as it was, enclosed in a shell - the clinical manifestations gradually decreased.
Causes of osteonecrosis
Within each existing theory of the development of osteonecrosis, different causes are accepted as the cause for the onset of the disease, e. g. , mechanical trauma, genetic predisposition or disorder. metabolism. A particular difficulty in determining the cause of osteonecrosis is that the disease can occur in both the elderly and the young, both healthy and poorly exercised. There is a widespread belief that the cause of osteonecrosis is the deposition of salts in the spine: supposedly on X-rays, salts can be seen as "growing" or "hooking" on the vertebraeliving. If during movement there is a crunch and crunch in the joints, as if sand is poured between them, then for many patients the only reason for this condition is the notorious "salt deposition". Such misconceptions are not at all harmless: the correct idea of \u200b\u200the ways of treating the disease can be determined based on the analysis of the causes of the disease.
The term "osteochondrosis" comes from the Greek roots osteon - "bone" and chondr - "cartilage". The ending "-oz" means that the disease of bones and cartilage is not related to the inflammatory process, is degenerative-dystrophic in nature, that is, the basis of the disease is malnutrition of the tissues and the consequencesis the degeneration of its structure. Like all living tissues, the bony tissue of the vertebrae and the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs are constantly rearranging and renewing themselves. Under the influence of regular physical activity, they gain strength and elasticity, and when there is no load, the strength of the tissues decreases.
This is due to the peculiarities of nutrition and blood supply to bone and cartilage tissues. Adult discs do not have their own vessels; they receive nutrients and oxygen from nearby tissues. Therefore, for proper nutrition to the discs, it is necessary to activate blood circulation in the tissues surrounding the discs. And this can only be achieved through intense muscular activity.
According to its structure, the disc can be divided into two parts: this is the glue core that gives the disc its elasticity, located in the center and the strong fibrous capsule surrounding it. Due to the nutritional depletion of the intervertebral discs, the complex structure of the biopolymer compounds that make up the pulp nucleus is destroyed. The moisture in the glue core is reduced and it is easier to break. When exposed to even small overloads, the gelatinous filling can disintegrate into pieces. This leads to an even greater decrease in its elasticity. There is also a decrease in the strength of the annulus fibrosus. All these factors form the basis and cause for the development of osteonecrosis.
In order to restore the function of the spine, leaving scars due to disc damage, it is necessary to mobilize the compensatory capabilities of the spine, as well as of the entire musculoskeletal system in general, rather than reabsorption of"salt deposits" or the removal of "spikes" on the vertebrae. When conducting X-ray examination after the end of treatment, it can be seen that the vertebrae have not changed shape. And the infamous "spikes" are not the cause of osteonecrosis but the result of adaptation. Marginal growth increases the supporting surface area of the vertebral body. By increasing the area, the specific pressure decreases, which can compensate for the decrease in disc strength and elasticity.
The degenerative-dystrophic changes occurring in the spine are accompanied by calcification (calcification) of damaged intervertebral discs, individual parts of articular ligaments, cartilage, capsules. This process can only be called salt deposition. Thus, this is not the cause of osteonecrosis but only the consequence and the final stage of the above process.
The reverse development of structural changes in the spine is almost impossible. But keeping them to a minimum is a very real challenge. If no effort is made to maintain the spine in the condition it achieved with treatment, the pain may recur.
Clinical manifestations of osteonecrosis
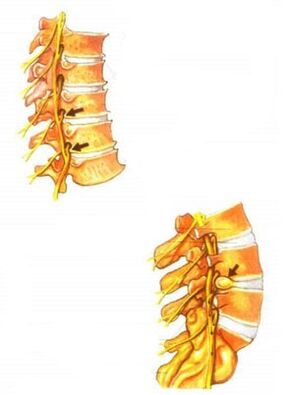
The clinical manifestations of osteonecrosis are diverse. They depend on the stage of development of osteonecrosis. The main clinical symptoms of osteonecrosis occur when the pathological process extends to the posterior portion of the annulus and posterior longitudinal ligament. Depending on the stage of degeneration of the discs, irritation, compression or impaired conduction of the spinal roots, vessel or spinal cord compression occurs. Various neurological syndromes develop - reflex and compression.
The main cause of pain in osteonecrosis is the so-called nerve root irritation. In this case, circulatory disturbance occurs, edema occurs and in the future it is possible to develop fibrosis of the surrounding structures, accompanied by an increase in the sensitivity of the roots to various influences. (motion in the affected segment of the spine, etc. ).
Vascular disturbances in osteonecrosis are often associated with impaired vasomotor capacity. Mechanical compression of blood vessels by bone-forming substances in the cervical spine may also occur.
Symptoms of osteonecrosis
One of the features of osteonecrosis of the spine that exacerbates this process is its overly extensive symptomatology. The disease can manifest in completely different parts of the body. It can be pain or numbness in the extremities or confusion and pain in the internal organs. At the same time, a person is usually not associated with pain in the heart region, abnormalities in the functioning of the genital organs, headaches, pain and numbness in the legs with osteonecrosis, and in general with the spine, dealing withtreat" the symptoms of osteonecrosis directly with the help of pain relievers, all advertised drugs, dietary supplements and other methods. But this path only aggravates the situation. Osteochondrosis continues to evolve and the treatments used, at best, simply do not lead to significant improvement, except for temporary pain relief, and in the worst cases, they can cause further harm to the patient. body.
Therefore, it is important to carefully analyze your condition and the changes taking place in it. It is necessary to start on the right track: consult a doctor in time, undergo the necessary diagnoses, and only after determining the correct diagnosis, begin treatment under the supervision of the attending physician.
The main symptoms of osteonecrosis include, first of all, pain and discomfort in the back. At the same time, the pain can be cyclical, unstable, appearing now, then disappearing. But the first feeling of discomfort or pain in the spine will make you think. The appearance of the first pains is a signal that you must at least pay attention to it, try to recall why they appear. This can be caused by lifting a heavy object, sudden movements, falls, etc. v.
Another symptom of osteonecrosis is accompanied by discomfort or back pain with pain and numbness of the extremities (arms or legs). The pain often radiates to the left limb, i. e. to the left arm or leg. In addition, pain can manifest itself in the heart region, in the back, and not only in the spinal region, but, for example, in the ribs, etc. v. It is especially important in this case to pay attention to the nature of the pain variation depending on the patient's actions, comparing pain sensation in the back with pain, for example, in the legs. If the patient sits for a long time and has pain or numbness in the legs, discomfort in the lower back, after warming up or walking a little the pain has disappeared, this will be an indirect sign. lumbar osteochondrosis of the spine. Similar images can be with the neck and arms. In summary, we can say that the main symptoms of osteonecrosis include pain and discomfort in the back. In cases where these symptoms are concurrent with pain in other parts of the body, osteonecrosis can be complicated by protrusion of the eye, disc herniation, and nerve compression.
In addition, I would like to note that even at the first appearance of pain in the spine, special attention should be paid to this unpleasant condition. After all, osteonecrosis can manifest itself weakly or not for a long time. At the same time, it will continue to successfully grow in the spine, leading to degeneration of an increasing number of discs. Therefore, a timely visit to the doctor will allow the diagnosis of osteonecrosis at an earlier stage, which will greatly facilitate the treatment.
Osteonecrosis and salt deposition
Osteophytes, or hook-like growths of the vertebrae, appear to reduce the load on the intervertebral discs. In this case, the presence of osteoblasts harms the mobility of the disc joints.
The conventional view in everyday life that salt deposition is the primary cause of osteonecrosis is misguided. Therefore, it makes no sense to treat osteonecrosis with a salt-free diet.
The most common complaints of osteonecrosis of the spine
The most common complaints in osteonecrosis are as follows:
- Discomfort in different parts of the spine. Pain can vary from mild, dull, pulling to strong, sometimes very intense and intolerable - accompanied by low back pain.
- Increased fatigue at work, both physical and mental.
- Impaired sensation in the limbs and different parts of the body, cold hands or feet.
- Pain radiates down the leg, along the nerves.
- Pain spreads to the shoulder blades and shoulders, as well as pain in the neck and back of the head.
- Frequent companions of cervical fibroids are headaches, dizziness. Often observed visual fatigue increased or decreased visual acuity.
- With the defeat of the lumbar-sacral region, disorders of the reproductive system are common - various sexual dysfunctions. Therefore, in most men, after treatment there is an increase in sexual power. In women, the normal functioning of the luminescence increases the chances of conception and contributes to a comfortable pregnancy.
Diagnosis of osteonecrosis
To diagnose osteonecrosis, it is necessary to collect a medical history. In this case, it is important to establish patient complaints. Some of the symptoms of osteonecrosis are quite typical. On the other hand, others must be distinguished from signs of other diseases. Importantly, the neurological, vascular, and nutritional disturbances occurring in osteonecrosis can mimic various diseases, such as angina, gastritis, peptic ulcers, surgical diseases, etc. Acute surgery of intra-abdominal organs. Therefore, to avoid misdiagnosis and subsequent prescribing of the wrong treatment, each symptom must be analyzed in detail.
When collecting the medical history, including the patient's complaints, the current medical history and the patient's life, the physician pays attention to his age, since osteonecrosis develops more often in humans. age and the course of symptoms from onset until the patient's visit to the doctor. For osteonecrosis, a slow development is characteristic, in which periods of exacerbation are periodically replaced by periods of remission. Additional research methods are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
X-ray examination for osteonecrosis
The most accessible and at the same time quite informative method of diagnosing osteonecrosis is X-ray examination. There are several types of X-ray methods for diagnosing this disease:
Simple spine X-ray is the simplest X-ray method to diagnose osteonecrosis. Its essence lies in taking X-rays of the entire spine or its individual segments. Usually, a visible radiograph is performed - based on the symptoms of the disease and the patient's complaints, the location of the spinal lesion is determined. On the X-ray image of the spinal segment affected by osteonecrosis, one can see a decrease in the thickness (atrophy) of the intervertebral discs, which manifests as a decrease in the space between the vertebrae, a bony appearance. outgrowth of the vertebral body - bone formation, partial dissolution - destruction of the bony tissue of the vertebral body, a change in the shape of the spinal segment, for example, lumbar lubrication.
Myelography is a more complex and dangerous diagnostic method. During such an examination, a certain amount of contrast fluid is injected into the spinal canal. The risks of this test are the possibility of an allergic reaction to the contrast material or the risk of spinal cord injury during the lumbar puncture. A myelogram can determine the internal structure of the spinal canal. This method is particularly informative for identifying spinal hernias.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are the most modern, but also the most expensive and inaccessible methods of diagnosing osteonecrosis. These diagnostic methods are often used when it is necessary to distinguish between osteonecrosis and other diseases of the spine with similar symptoms, for example, tumors of the spinal canal.
To comprehensively assess the patient's condition, it is imperative to conduct a neurological examination of the patient with osteonecrosis. Thanks to neurological consultation, it is possible to clarify the localization and extent of motor and sensory disorders.
Treatment of osteonecrosis
The clinic offers effective treatment for all forms of osteonecrosis. Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The treatment is based on a comprehensive program aimed at rapidly eliminating the underlying syndrome and the cause of the distress. As part of complex therapy, the following methods can be used:
- Acupuncture;
- vacuum therapy;
- gentle manual therapy technique (relaxation after isometric);
- laser therapy;
- Acupuncture;
- dry traction;
- magnetism;
- electrical stimulation and other treatments.
The average treatment course is 10-15 sessions, eliminating acute pain syndrome from 1 to 3 sessions.
The sooner treatment begins, the better the results will be!
Is complete removal of osteonecrosis real?
It depends on the type of disease, the severity, the right way and timely treatment. It is completely curable in the early stages.
But it is possible to prevent the exacerbation of osteonecrosis, leaving no pain for many years. If a person has osteonecrosis, but he does not feel discomfort now, this does not mean that he has passed without leaving a mark. There may be changes in the spine.
The main task is to stop the development of the disease and to do everything so that some pathological changes in the spine disappear, symptoms disappear or reduce (back pain, colds and numbness of hands and feet, headache, etc ) ).





































